- Veeam Support Knowledge Base
- Azure VMware Solution Support — Considerations and Limitations
Azure VMware Solution Support — Considerations and Limitations
Cheers for trusting us with the spot in your mailbox!
Now you’re less likely to miss what’s been brewing in our knowledge base with this weekly digest
Oops! Something went wrong.
Please, try again later.
Challenge
Azure VMware Solution (AVS) is a VMware Cloud Verified offering that requires specific considerations to work with Veeam Backup & Replication. Aside from the listed instructions and limitations below, you can use AVS with Veeam Backup & Replication like you would any other VMware vSphere environment.
Some VMware features and permissions are not available upon deployment. This means some features in Veeam Backup & Replication are limited or unavailable. Depending on update releases, this situation may change, and features in the table below may become available.
Solution

Implementation Step 1 - VMware Azure Solution
- Deploy and access AVS.
After deploying AVS, you will end up with an AVS private cloud resource and an Azure virtual network associated with it. If you have not done so, you will need to provision an externally accessible workload with access to this virtual network. Review: Microsoft - Learn how to access an AVS private cloud and Microsoft - Configure networking for your AVS private cloud. - Ensure you have network services configured.
You will need to deploy DHCP and DNS. You may also wish to configure an identity provider.
For this, your Hub virtual network will act as a central point of connectivity between your on-premises network, your other Azure-native services, and your AVS private cloud. For an architecture overview, please reference Microsoft - Learn how AVS integrates with native Azure services. - Create a DHCP server.
Create a DHCP server on NSX. Be sure to add an NSX-T network segment if you have not already done so and change its default DNS settings under Advanced Networking & Security. Review: Microsoft - Create and manage DHCP in AVS
(Note that it is possible to use a local DHCP server in the private cloud instead of the NSX-integrated option, but you would not want to use external DHCP and route broadcast DHCP traffic over the WAN.) -
Configure a DNS service.
For Azure DNS resolution, it is recommended you configure an AD domain controller and Azure DNS private zones. Microsoft - AVS DNS Resolution Considerations
Be sure to configure DHCP in the step above to point directly to this local DNS server or Azure DNS.
(Optionally, you can configure a DNS forwarder service on NSX, ensure your NSX Tier-1 Gateway is associated with your edge cluster, allowing you to configure stateful services. Set up a DNS zone for your NSX deployment and then create a DNS forwarder service. VMware - Add a DNS Forwarder Service.) - Configure an identity provider in the Azure portal.
Configure vCenter SSO to point to the same AD domain controller as in the previous step. This can be integrated using Azure AD Connect for identity purposes. Microsoft - AVS Identity Sources - Configure external storage
For virtual machine storage, if you want to use something besides VSAN, you can configure third-party datastores. Veeam will be able to read data from these datastores for processing, for example:- Azure NetApp Files
- Azure Elastic SAN
Note that for some third-party storage implementations, additional networking is configured on AVS. These network switches are used for storage traffic but, depending on the environment may be partially visible using standard permissions. You can ask Microsoft Support to fully hide these network switches from the vCenter credentials used or contact Veeam Support for a hotfix that ignores switches it does not fully have access to.
For backup storage, see Implementation Step 5 — Add Veeam Repository. When writing to a local target, make sure to use a local disk, not a file share mount. For example, using Azure Blob or Azure Files via an NFS mount to send backup data to from Veeam Backup & Replication is not supported.
Implementation Step 2 - Veeam Backup & Replication
- Use a new Windows Server virtual machine and install Veeam Backup & Replication. This can be deployed within any AVS or on-premises datacenter environment, if network connectivity exists between it and the AVS vCenter as well as other Veeam servers if needed, or other virtual machines for guest processing.
- Ensure DNS settings are configured so that this server can resolve the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the AVS vCenter Server.
- Check the below information carefully for known limitations and configuration steps before you proceed.
Implementation Step 3 - Add VMware vCenter
Add vCenter to the Veeam console. Review: Veeam - Adding VMware vSphere Servers
- When adding a vCenter server, specify the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) that ends with avs.azure.com.
- Use the cloudadmin@vsphere.local user, or create a vCenter User with the required permissions.
Implementation Step 4 - Add Veeam Proxy
- Backup Proxy: This role can be handled by the Veeam Backup Server or by dedicated Windows VMs in the same environment. Ensure that you have the appropriate resources allocated to handle your backup requirements.
Note: Linux-based Backup Proxies cannot be used with AVS because they do not detect the VMware Cloud Specific specific logic. - Transport Mode: Virtual Appliance (HotAdd) transport mode will be used by default. Depending on the environment, it may be possible to use NBD or NFS transport modes. For example, NFS transport can be used to protect workloads running on Azure NetApp Files. If you are protecting a workload with multiple disks that require different transport modes for backup, the backup may fail if the failover to network mode option is not enabled.
Implementation Step 5 - Add Veeam Repository
- As AVS only comes with production storage options, we do not recommend using this to also store backups. An external backup location is needed. You could, for example, achieve this by sending data directly to Azure Blob if applicable, or use an Azure-native VM as a backup target and then tier to Azure Blob, or by sending backup data to a repository in a different location depending on the bandwidth and throughput available.
- You may need to ensure network security groups allow Veeam repository traffic. Veeam – Backup Repository Connections.
Implementation Step 6 - Add Secondary Backup Target
Following the 3-2-1 rule, it is recommended to create a backup copy to an additional location. There are several ways to achieve this:
- Veeam Scale-out Backup Repository - Capacity Tier usage. In copy mode this feature can be used to create additional backup copies on Azure Blob storage. Please use a private endpoint for Azure Blob to minimize data transfer costs.
- Veeam Backup Copy Job to on-premises or Veeam Cloud Connect (Enterprise). There is no special configuration required aside from network connectivity and firewall rules. For standard Backup Repository usage, it is recommended to create a VPN tunnel or use an ExpressRoute circuit from AVS to the on-premises datacenter.
Additional Scenarios
- Restore external backups to AVS. For this to work you will need to have Veeam Backup & Replication connected to vCenter and a working proxy (can be default) (implementation steps 1-4).
Data can be restored from on-premises workloads and Azure-native VM workloads. Note that restore functionality that requires conversion may need to be staged to on-premises VMware infrastructure first. - Veeam VM Replication to AVS. For this to work you will need to have Veeam Backup & Replication connected to the source as well as the target vSphere infrastructure, and have a working proxy and repository (implementation steps 1-5).
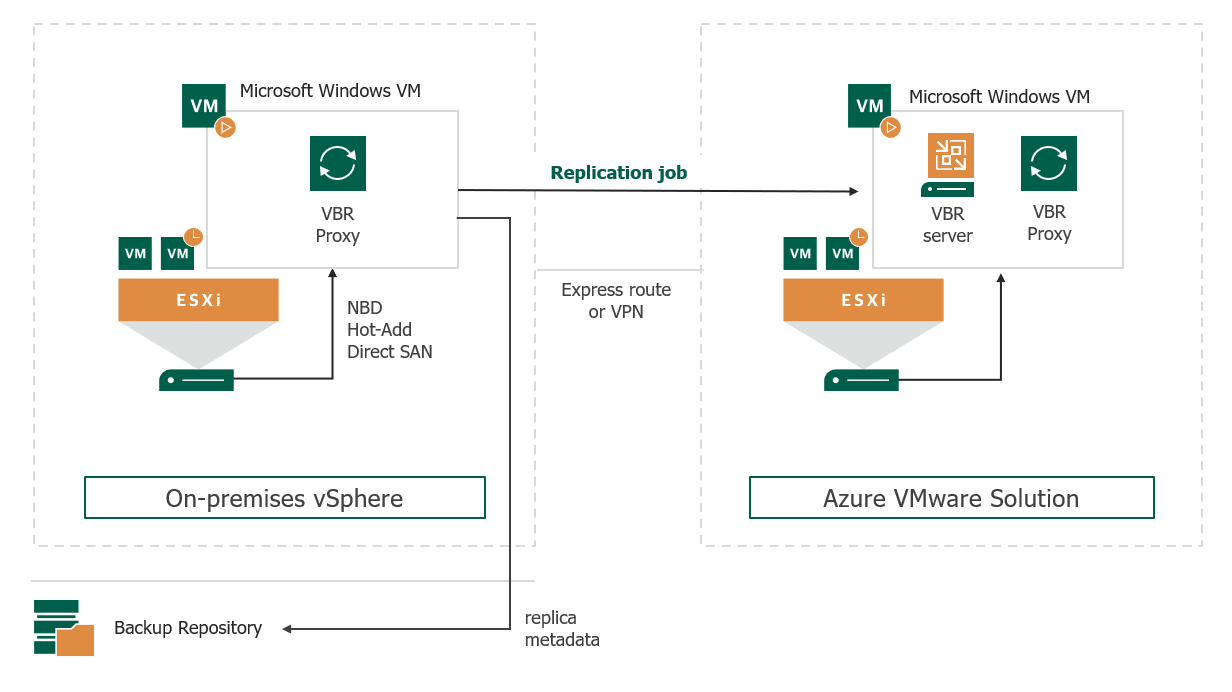
The Veeam Repository for replication data can be hosted on the AVS vSAN datastore. Note that it is not recommended to use this same production datastore to also store backup data, this should be separate to maintain data resiliency.
It is possible to replicate from on-premises VMs to AVS, from AVS to AVS, and from AVS back to on-premises.
Azure VMware Solution (AVS) specific issues and solutions
Issue
Veeam Backup & Replication may stop working after AVS is automatically updated.
Solution
- Please check this article for the minimum required Veeam Backup & Replication version or patches.
- For customers with socket-based licensing, make sure that any newly deployed ESXi hosts receive Veeam licenses. Potentially older ESXi hosts need to be revoked from consuming a license. We recommend using Veeam Universal Licensing to avoid any specific license issues with AVS.
Issue
Some Veeam Backup & Replication features are not available due to limitations with VMware Cloud Verified solutions like AVS (compared with on-premises VMware vSphere infrastructure).
Solution
|
Affected Veeam Feature |
Limitation |
Workaround |
|
Instant VM Recovery |
Currently, AVS does not allow NFS access to the backup server |
Use a combination of Veeam backup jobs and replication jobs for proactive restore capabilities. |
|
Other OS File Level Recovery |
Currently, AVS does not allow NFS access to the backup server |
Start Linux File Level Recovery with a Linux server helper host instead of a temporary helper appliance. |
|
SureBackup, Sure Replica, OnDemand Labs, Virtual Lab |
Currently, AVS does not allow NFS access to the backup server and network manipulation |
SureReplica is available if the replication target is a non-VMware Cloud vSphere environment (i.e., you can replicate a VM from AVS to on-premises) |
|
VM Replication Network Mapping |
Requires NSX 2.5.3.4 or higher |
|
|
VM Replication-based File Level Recovery |
|
Use a file restore from backup or a VM replica to start the File-Level Recovery. |
|
Replication (where Azure-based repository is used to store replica metadata) |
Due to a lack of permissions, the repository Data Mover cannot connect to the Veeam server. |
Enable the "Run server on this side" option for the repository. For Windows repositories, it can be found under Ports configuration. For Linux - under Advanced settings in the server configuration wizard. |
|
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) Replication |
Currently, CDP is not supported on AVS |
|
More Information
- Learn how to access an AVS private cloud - Microsoft Documentation
- Configure networking for your AVS private cloud – Microsoft Documentation
- Learn how AVS integrates with native Azure services - Microsoft Documentation
- Create and manage DHCP in AVS - Microsoft Documentation
- Add a NSX DNS Forwarder Service - VMware Documentation
To report a typo on this page, highlight the typo with your mouse and press CTRL + Enter.
Spelling error in text
Thank you!
Your feedback has been received and will be reviewed.
Oops! Something went wrong.
Please, try again later.
You have selected too large block!
Please try select less.
KB Feedback/Suggestion
This form is only for KB Feedback/Suggestions, if you need help with the software open a support case
Thank you!
Your feedback has been received and will be reviewed.
Oops! Something went wrong.
Please, try again later.